1. Introduction to Decarbonization Strategy
Defining 'Decarbonization Strategy' for Businesses and Industrial Bodies
A decarbonization strategy is a comprehensive plan implemented by businesses and industrial bodies to reduce carbon emissions associated with their operations. It involves a systematic approach to identifying, designing, and executing projects and policies that lower the carbon footprint of an organization. This can involve multiple avenues such as energy efficiency, renewable energy sourcing, process & technology improvements, carbon capture, etc.
These strategies are framed bearing in mind an entity's specific needs, regulatory requirements, and larger climate objectives – the ultimate goal being achieving an operational mode that emits minimal to zero carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
Why Implementing a Decarbonization Strategy is Crucial for the Future
Implementing a decarbonization strategy is no longer just an option but a necessity. Climate change, caused by escalating levels of greenhouse gases, threatens our planet's balance and future. Here’s why decarbonization is crucial:
- Climate Responsibility: Industries are some of the most significant carbon emitters, contributing to the acceleration of climate change. According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), industrial activities account for approximately 21% of global greenhouse gas emissions. Therefore, it is crucial for industries to proactively participate in reducing emissions to mitigate the impacts of climate change.
- Regulatory Compliance: Governments worldwide are increasingly setting mandatory carbon reduction targets as part of their efforts to combat climate change. By decarbonizing their operations, industries can ensure compliance with these regulations and avoid potential penalties or legal consequences. For example, the European Union's Emissions Trading System (EU ETS) requires companies to monitor and report their greenhouse gas emissions, and non-compliance can result in fines.
- Cost Savings: Implementing energy-efficient operations and utilizing renewable energy sources can provide significant cost benefits for industries in the long run. According to a study by the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), transitioning to renewable energy sources could save businesses $60 billion and $160 billion annually by 2030. Additionally, energy-efficient practices can lead to reduced energy consumption and lower utility bills, resulting in substantial cost savings over time.
- Reputation Management: Consumers and stakeholders are becoming increasingly aware and concerned about businesses' environmental impacts. Failing to exhibit sustainable practices can harm a company's reputation and lead to a loss of trust among consumers. On the other hand, a firm commitment to environmental protection and sustainable practices can enhance a company's brand image and attract environmentally conscious consumers. For example, a 2021 study by the University of Michigan found that companies that are perceived to be sustainable are more likely to be seen as trustworthy and innovative.
- Investment Opportunities: The rise of green finance and impact investing has created new opportunities for businesses prioritizing sustainability. Investors are increasingly looking for companies that align with their environmental and social values, and those businesses are more likely to attract investment. According to the Global Impact Investing Network (GIIN), the impact investing industry reached USD $715 billion in 2020, up from $502 billion in 2016. This estimate has been updated to USD $1.165 trillion in 2022, marking the first time this figure crosses the $1 trillion mark. By prioritizing sustainability, businesses can tap into this growing market and access additional funding sources.
Adopting a decarbonization strategy is a win-win proposition, capable of bettering the environment while providing businesses smart ways to grow. It's time industries saw it not as an obligation, but an opportunity.
2. Components of a Decarbonization Strategy
What is the Process of Creating a Decarbonization Strategy?
Creating an effective decarbonization strategy typically follows a multi-step process:
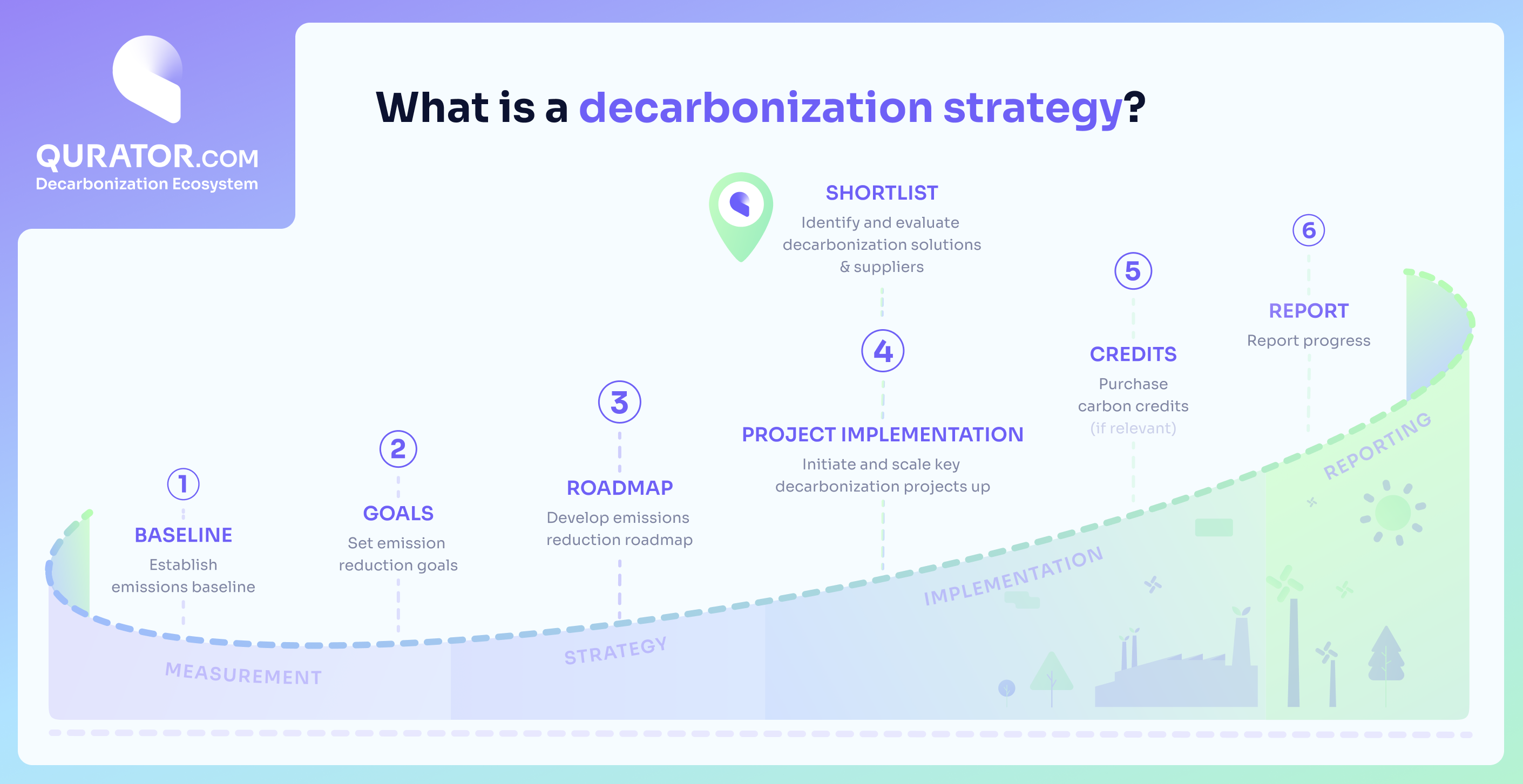
- Baseline Assessment: Companies must first understand their current Scope 1, 2, 3 and even 4 emissions through a carbon footprint analysis.
- Goal Setting: This involves setting clear, measurable targets for reducing emissions, often in alignment with international standards, such as the Paris Agreement.
- Strategy Development: Developing an emissions reduction roadmap by identifying and prioritizing actions that can most effectively and efficiently reduce emissions.
- Project Implementation: This phase involves the execution of the planned initiatives to achieve the set goals.
- Monitoring and Reporting: Continuous tracking of progress against targets and transparent reporting enhances accountability and helps refine the strategy over time.
Methods and Services Employed to Achieve Decarbonization Goals
Each sector has its own methods and strategies, which can include renovation of buildings for energy efficiency, implementation of renewable energy resources, use of cleaner fuels, and deployment of electrification and carbon capture technologies. To reduce their carbon emissions, companies typically utilize a range of methods and services, depending largely on the kind of industries and emission scope (1, 2, 3, or 4) they aim to tackle. Service and manufacturing companies usually have different emission reduction focuses. Some common methods include:
- Energy Efficiency Improvements: Upgrading to more efficient equipment and optimizing processes.
- Renewable Energy Sources: Switching to solar, wind, or hydroelectricity to power operations.
- Carbon Capturing: Investing in carbon capture and storage (CCS) technologies.
- Green Supply Chain Management: Ensuring that suppliers adhere to environmentally friendly practices.
- Employee Engagement and Training: To foster a culture of sustainability within the organization.
Finding suitable vendors with decarbonization solutions one can trust is a vital part of any decarbonization strategy. By using a platform like Qurator, one can easily discover and evaluate decarbonization solutions suitable for a wide range of industries. See our open marketplace.
3. The Role of Technology and Innovation in Decarbonization Strategies
Innovation and technology play a crucial role in decarbonization strategies, as they provide the means to achieve reduction of greenhouse gases. These innovations can be pertaining to deployment of renewable energy, electrification of transport, changes to industrial processes, and the development of carbon capture and storage (CCS).
Digital technologies can also aid decarbonization. For example, smart grids can balance supply and demand across the network, reducing the need for fossil fuel power stations. Additionally, advancements in AI and machine learning can provide data and analytics to optimize energy usage and identify inefficiencies.
Explore more technologies on the Qurator Marketplace >>
4. Conclusion
A decarbonization strategy is no longer a nice-to-have but a must-have for any forward-thinking business. It's an investment in the future that promises economic, environmental, and social dividends. As global consensus shifts towards a greener economy, businesses that lead in decarbonization efforts will not only contribute to a healthier planet but will also likely reap the benefits of resilience and relevancy in an evolving marketplace.




